Testowanie REST API z Serenity i Rest-assured
Zaktualizowaliśmy ten tekst dla Ciebie!
Data aktualizacji: 27.08.2024
Autor aktualizacji: Marcin Łącki
Rest-assured to framework w Javie służący do testowania i walidacji REST API.
Serenity to framework do automatycznego testowania akceptacyjnego oparty na BDD (Behavior Driven Development). Połączenie Rest-assured z Serenity umożliwia łatwe tworzenie testów API w stylu BDD oraz generowanie estetycznych i przejrzystych raportów.
Projekt testowy
W ramach tego artykułu testowane będzie API postcodes.io.
Postcodes to darmowe, otwarte API dla kodów pocztowych i geolokalizacji w Wielkiej Brytanii.
Struktura projektu
Projekt używa standardowej struktury Maven.
postcodes-api-tests
src
pom.xml
test
java
pl.jlabs
cukes
RunCukes.java
stepdefs
BaseTest.java
NearestPostcodesSteps.java
RandomPostcodeSteps.java
ValidatePostcodeSteps.java
PostcodesEndpoints.java
resources
features
NearestPostcode.feature
RandomPostcode.feature
ValidatePostcode.featurepom.xml
<!--?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?-->
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemalocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelversion>4.0.0</modelversion>
<groupid>pl.jlabs</groupid>
<artifactid>restassured-serenity</artifactid>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<restassured.version>3.3.0</restassured.version>
<hamcrest.version>1.3</hamcrest.version>
<json.version>20180813</json.version>
<serenity.version>2.0.81</serenity.version>
<serenity.maven.version>2.0.81</serenity.maven.version>
<serenity.cucumber.version>1.0.21</serenity.cucumber.version>
<cucumber.version>4.2.0</cucumber.version>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<parallel.tests>4</parallel.tests>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-core</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupid>io.cucumber</groupid>
<artifactid>cucumber-core</artifactid>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>io.cucumber</groupid>
<artifactid>cucumber-java</artifactid>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>io.cucumber</groupid>
<artifactid>cucumber-junit</artifactid>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-junit</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-rest-assured</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-cucumber4</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>junit</groupid>
<artifactid>junit</artifactid>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.assertj</groupid>
<artifactid>assertj-core</artifactid>
<version>3.6.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.hamcrest</groupid>
<artifactid>hamcrest-all</artifactid>
<version>1.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupid>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupid>
<artifactid>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactid>
<version>2.22.1</version>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactid>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactid>
<version>2.22.1</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*Cukes.java</include>
</includes>
<parallel>classes</parallel>
<threadcount>${parallel.tests}</threadcount>
<forkcount>${parallel.tests}</forkcount>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupid>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupid>
<artifactid>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactid>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupid>net.serenity-bdd.maven.plugins</groupid>
<artifactid>serenity-maven-plugin</artifactid>
<version>${serenity.maven.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>serenity-reports</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Serenity jest kompatybilne z Cucumber w wersjach 2.x i 4.x. Aby używać Cucumber w wersji 4.x, należy wykluczyć cucumber-core z serenity-core.
Pluginy Maven failsafe oraz serenity-maven-plugin muszą być odpowiednio skonfigurowane, aby generować raporty testów.
PostcodesEndpoint.java
Został stworzony Enum z adresami URL dla endpointów.
package pl.jlabs;
public enum PostcodesEndpoints {
NEAREST("postcodes?lon={lon}&lat={lat}"),
RANDOM("/random/postcodes"),
VALIDATE("postcodes/{postcode}/validate");
private final String url;
PostcodesEndpoints(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
}RunCukes.java
Runner testów Cucumber.
package pl.jlabs.cukes;
import cucumber.api.CucumberOptions;
import net.serenitybdd.cucumber.CucumberWithSerenity;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
@RunWith(CucumberWithSerenity.class)
@CucumberOptions(
plugin = {"pretty"},
features = "classpath:features",
glue = {"pl.jlabs.stepdefs"}
)
public class RunCukes {}
NearestPostcodesSteps.java
package pl.jlabs.stepdefs;
import PostcodesEndpoints;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Given;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Then;
import cucumber.api.java.en.When;
import net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import static net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest.restAssuredThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.*;
public class NearestPostcodesSteps extends BaseTest {
private static final Map<string,object> VALID_GPS_DATA = Stream.of(
new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>("lon", "0.629834723775309"),
new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>("lat", "51.7923246977375"),
new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>("postCodes", new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("CM8 1EF", "CM8 1EU", "CM8 1PH", "CM8 1PQ"))))
.collect(Collectors.toMap(AbstractMap.SimpleEntry::getKey, AbstractMap.SimpleEntry::getValue));
private static final List<string> COORDINATES_OUTSIDE_UK = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("50.049683", "19.944544"));
@Given("the request with valid coordinates to the Nearest Postcodes endpoint")
public void theRequestWithAValidCoordinatesToTheNearestPostcodesEndpoint() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lon"))
.pathParam("lat", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lat"));
}
@Given("the request with invalid longitude")
public void theRequestWithInvalidLongitude() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(3))
.pathParam("lat", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lat"));
}
@Given("the request with valid coordinates outside UK")
public void theRequestWithAValidCoordinatesOutsideUK() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", COORDINATES_OUTSIDE_UK.get(0))
.pathParam("lat", COORDINATES_OUTSIDE_UK.get(1));
}
@Given("the request with invalid latitude")
public void theRequestWithInvalidLatitude() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lon"))
.pathParam("lat", RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(3));
}
@When("the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint")
public void theRequestIsMadeWithGetMethod() {
SerenityRest.when().get(PostcodesEndpoints.NEAREST.getUrl());
}
@Then("the response with a correct list of postcodes is returned")
public void theResponseWithACorrectListOfPostcodesIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", hasSize(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).size()))
.body("result[0].postcode", equalTo(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).get(0)))
.body("result[1].postcode", equalTo(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).get(1)))
.body("result[2].postcode", equalTo(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).get(2)))
.body("result[3].postcode", equalTo(((List) VALID_GPS_DATA.get("postCodes")).get(3))));
}
@Then("an empty result list is returned")
public void anEmptyResultListIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", is(nullValue())));
}
@Then("the invalid longitude latitude submitted error is returned")
public void theInvalidLongitudeLatitudeSubmittedErrorIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_BAD_REQUEST)
.body("status", equalTo(HttpStatus.SC_BAD_REQUEST))
.body("error", equalTo("Invalid longitude/latitude submitted")));
}
}
Serenity udostępnia klasę SerenityRest do korzystania z Rest-assured.
Dla zastosowania BDD (Behavior Driven Development), SerenityRest jest używana dwukrotnie. W kroku Given:
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("lon", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lon"))
.pathParam("lat", VALID_GPS_DATA.get("lat"));oraz w kroku When, gdzie wykonuje się wywołanie do API:
SerenityRest.when().get(PostcodesEndpoints.NEAREST.getUrl());W celu przeanalizowania odpowiedzi wywoływana jest metoda restAssuredThat z SerenityRest:
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_BAD_REQUEST)
.body("status", equalTo(HttpStatus.SC_BAD_REQUEST))
.body("error", equalTo("Invalid longitude/latitude submitted")));Można dokonać również asercji przy użyciu obiektu SerenityRest:
SerenityRest.then()
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", is(notNullValue()));RandomPostcodeSteps.java
package pl.jlabs.stepdefs;
import PostcodesEndpoints;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Given;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Then;
import cucumber.api.java.en.When;
import net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import static net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest.restAssuredThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.notNullValue;
public class RandomPostcodeSteps extends BaseTest {
@Given("a request to the random postcodes endpoint")
public void aRequestToTheRandomPostcodesEndpoint() {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI);
}
@When("the request is made with the get method to random postcode")
public void theRequestIsMadeWithTheGetMethodToRandomPostcode() {
SerenityRest.when().get(PostcodesEndpoints.RANDOM.getUrl());
}
@Then("the randomly generated postcode is returned")
public void theRandomlyGeneratedPostcodeIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", is(notNullValue())));
}
}ValidatePostcodeSteps.java
package pl.jlabs.stepdefs;
import PostcodesEndpoints;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Given;
import cucumber.api.java.en.Then;
import cucumber.api.java.en.When;
import net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import static net.serenitybdd.rest.SerenityRest.restAssuredThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
public class ValidatePostcodeSteps extends BaseTest {
@Given("the request with a valid postcode")
public void theRequestWithAValid() {
validatePostCodeRequest(VALID_POST_CODES_LIST.get(0));
}
@Given("the request with an invalid postcode")
public void theRequestWithAnInvalidPostcode() {
validatePostCodeRequest(getRandomInvalidPostCode());
}
@Given("the request without postcode")
public void theRequestWithoutPostcode() {
validatePostCodeRequest("");
}
@When("the request is made with the get method to validate postcode")
public void theRequestIsMadeWithTheGetMethodToValidatePostcode() {
SerenityRest.when().get(PostcodesEndpoints.VALIDATE.getUrl());
}
@Then("the response with a result equal to {string} is returned")
public void theResponseWithAResultEqualToIsReturned(String expectedResult) {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.body("result", equalTo(Boolean.valueOf(expectedResult))));
}
@Then("the not found status code with an Invalid postcode error is returned")
public void theNotFoundStatusCodeWithInvalidPostcodeErrorIsReturned() {
restAssuredThat(response -> response
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_FOUND)
.body("error", equalTo("Invalid postcode")));
}
private void validatePostCodeRequest(String postCode) {
SerenityRest.given()
.baseUri(BASE_URI)
.pathParam("postcode", postCode);
}
}NearestPostcode.feature
Plik Feature z scenariuszami dla endpointu najbliższych kodów pocztowych:
Feature: Nearest postcode
Scenario: A correct list of postcodes is returned for valid coordinates
Given the request with valid coordinates to the Nearest Postcodes endpoint
When the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint
Then the response with a correct list of postcodes is returned
Scenario: An empty results list is returned for a valid coordinates outside UK
Given the request with valid coordinates outside UK
When the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint
Then an empty result list is returned
Scenario: An invalid longitude/latitude submitted error is returned for a request with invalid longitude
Given the request with invalid longitude
When the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint
Then the invalid longitude latitude submitted error is returned
Scenario: An invalid longitude/latitude submitted error is returned for a request with invalid latitude
Given the request with invalid latitude
When the request is made with the get method to nearest postcodes endpoint
Then the invalid longitude latitude submitted error is returned
RandomPostcode.feature
Plik Feature z scenariuszami dla generowania losowego kodu pocztowego:
Feature: Random postcode
Scenario: A random postcode is generated
Given a request to the random postcodes endpoint
When the request is made with the get method to random postcode
Then the randomly generated postcode is returned
ValidatePostcode.feature
Plik Feature z scenariuszami do walidacji kodu pocztowego:
Feature: Validate postcode
Scenario: True is returned for a request with a valid postcode
Given the request with a valid postcode
When the request is made with the get method to validate postcode
Then the response with a result equal to "true" is returned
Scenario: False is returned for a request with an invalid postcode
Given the request with an invalid postcode
When the request is made with the get method to validate postcode
Then the response with a result equal to "false" is returned
Scenario: Not found with an invalid postcode error is returned for a request without postcode
Given the request without postcode
When the request is made with get method to validate postcode
Then the not found status code with an Invalid postcode error is returned
Wykonanie testów
Aby uruchomić testy, użyj polecenia Maven:
mvn clean verify
Raport z testów
Po wykonaniu testów, w katalogu target/site/serenity zostanie wygenerowany raport. Aby go wyświetlić, otwórz plik index.html.
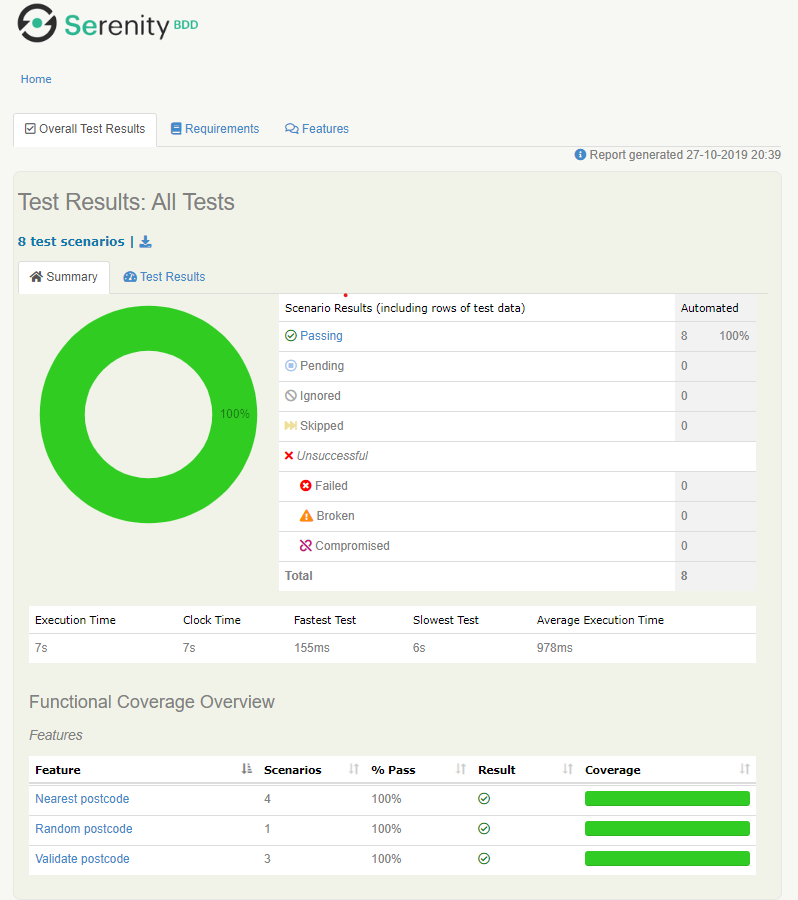
Raport wyświetlany jest w przyjaznej formie dla użytkownika.
W zakładce „Test Results” dostępne są szczegółowe raporty scenariuszy dla każdego przypadku. Poniżej raport dla scenariusza „True is returned for a request with a valid postcode”:
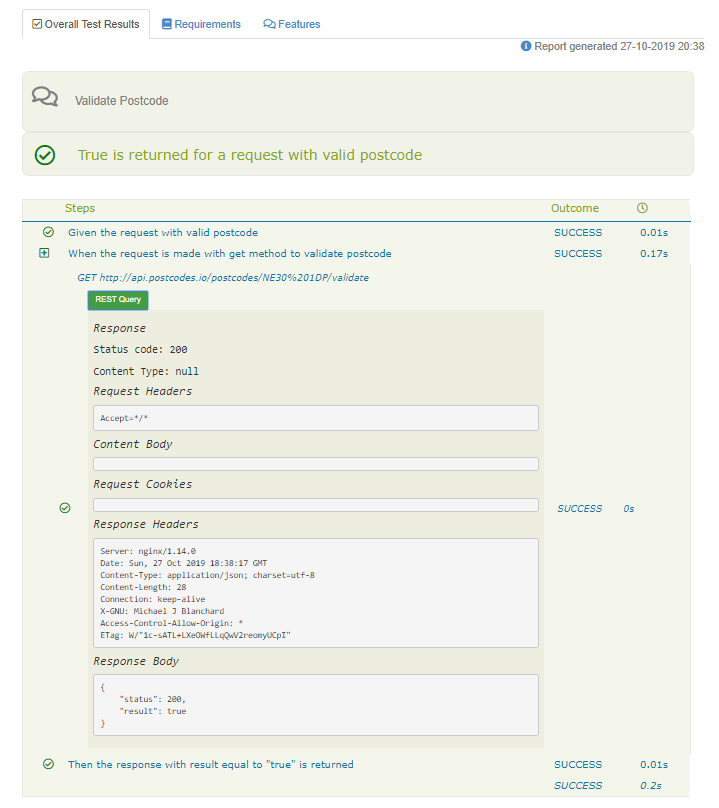
Przy użyciu przycisku „REST Query” można wyświetlić szczegóły zapytania. Widoczne są następujące szczegóły:
- Ścieżka (Path)
- Kod statusu (Status code)
- Nagłówki zapytania (Request Headers)
- Treść zapytania (Request Body)
- Ciasteczka zapytania (Request Cookies)
- Nagłówki odpowiedzi (Response Headers)
- Treść odpowiedzi (Response Body)
Podsumowanie
Serenity w połączeniu z Rest-assured tworzy idealny zestaw do tworzenia testów REST API w podejściu BDD. Implementacja testów jest prawie taka sama, jak w przypadku użycia samego Rest-assured, z niewielkim dodatkiem konieczności użycia obiektu SerenityRest jako „prefiksu”.
Ogromną zaletą Serenity są raporty, które zawierają pełne informacje o zapytaniach i odpowiedziach. Dodatkowo są przedstawione w przyjazny sposób co ma wpływ na szybkość ich analizowania.
Źródła
Poznaj mageek of j‑labs i daj się zadziwić, jak może wyglądać praca z j‑People!
Skontaktuj się z nami


